One of the most critical decisions facing many Americans as they approach retirement is when to start claiming Social Security benefits. For those who can afford to wait, the Social Security Age 70 Strategy offers an opportunity to maximize monthly benefits — with some individuals pushing their payouts to as much as $2,500 a month.

This article will explore the benefits of waiting until age 70, the delayed retirement credit, and how delaying Social Security can help provide a more financially secure retirement.
Social Security Age 70 Strategy
| Key Fact | Detail/Statistic |
|---|---|
| Full Retirement Age (FRA) | 66 or 67, depending on birth year |
| Increase for Delaying Until 70 | Up to 32% higher than FRA benefits |
| Average Monthly Benefit at 70 | $2,500+ depending on earnings history |
| Cost of Living Adjustments | Adjustments based on inflation (COLA) |
Why Waiting Until Age 70 Makes Sense
Social Security is a vital component of retirement income for millions of Americans, designed to replace a portion of pre-retirement income based on your earnings history. The amount you receive in benefits depends on when you begin claiming Social Security.
If you start collecting Social Security at your Full Retirement Age (FRA) — generally between 66 and 67, depending on your birth year — you’ll receive your full benefit amount. However, waiting until age 70 can significantly increase your monthly payout.
For example, a person who delays benefits until age 70 can receive up to 32% more than if they had claimed benefits at their FRA.
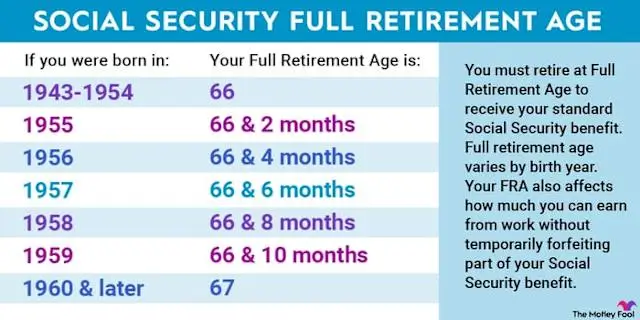
1. Delaying Benefits Increases Your Monthly Payment
The Social Security system rewards those who can wait to claim benefits by offering delayed retirement credits. These credits increase your benefit amount by about 8% per year for each year you delay claiming beyond your FRA, up to age 70.
If you start Social Security at age 70, you will receive your maximum monthly benefit, which could be as much as 32% higher than if you had begun claiming at age 66. For example, if your benefit at age 66 is $1,500, waiting until age 70 could increase your benefit to $1,980, or more, depending on your work history.
How the Delayed Retirement Credit Works
The delayed retirement credit boosts your monthly benefit by a fixed percentage for every year you delay starting your Social Security benefits beyond your FRA. The amount of the credit is 8% per year, which is the most significant increase the system offers.
Here’s a breakdown:
| Age | Monthly Benefit at FRA | Benefit with Delay (Age 70) |
|---|---|---|
| Age 66 (FRA) | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| Age 67 (1 year delay) | $1,500 | $1,620 |
| Age 68 (2 years delay) | $1,500 | $1,740 |
| Age 69 (3 years delay) | $1,500 | $1,860 |
| Age 70 (4 years delay) | $1,500 | $1,980 |
By delaying until age 70, you maximize your monthly benefit, helping provide greater financial security in retirement.
Social Security at Age 70: How Much Will You Receive?
On average, Social Security recipients who wait until age 70 can expect to see monthly benefits in the range of $2,500 or higher, depending on their earnings history. This amount is significantly higher than what someone would receive if they start claiming earlier.
For example, in 2025, the average monthly Social Security benefit for retirees who start at age 70 is estimated to be $2,500. For individuals with higher lifetime earnings, that amount could reach closer to $3,000 per month.
Social Security Benefit at Age 70 by the Numbers:
- Average benefit for high earners: Up to $3,000+ per month.
- Average benefit for the typical retiree: Around $2,500 per month.
- Benefit increase for waiting until age 70: Up to 32% more than at FRA.
Factors to Consider Before Delaying Social Security
While waiting until age 70 can result in higher monthly benefits, the decision to delay is not right for everyone. Several factors should influence your decision:
1. Health and Longevity
If you expect to live a long life, delaying Social Security benefits may be beneficial, as it maximizes the payout over time. On the other hand, if you have health concerns or expect a shorter life expectancy, claiming earlier may make more sense.
2. Spousal and Survivor Benefits
For couples, delaying Social Security may benefit the survivor. If one spouse claims later, the survivor may receive the larger of the two Social Security benefits after one spouse passes away. This strategy is particularly advantageous for higher-earning spouses.
3. Current Financial Needs
If you need immediate income in retirement, delaying Social Security until age 70 may not be a viable option. In this case, starting benefits earlier — even at age 62 — could be a better choice.
4. Social Security and Inflation
Social Security benefits are adjusted for inflation each year through COLA (Cost of Living Adjustments). This means that while delaying benefits results in a higher starting amount, inflation adjustments over time will continue to increase your benefits, providing long-term purchasing power.
The Pros and Cons of Waiting Until Age 70
While waiting until age 70 increases your monthly payout, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons before making this decision:
Pros of Waiting Until Age 70:
- Higher Monthly Benefits: Up to 32% more than starting at FRA.
- Maximizes Lifetime Payouts: Especially advantageous if you live into your 80s or 90s.
- Increased Survivor Benefits: Delaying may provide higher survivor benefits for your spouse.
Cons of Waiting Until Age 70:
- Short-Term Financial Strain: You may need to rely on other sources of income if you delay benefits.
- Uncertainty in Health: If you face health issues or a shorter life expectancy, the higher monthly benefits may not be fully realized.
Spousal and Survivor Benefits
In married couples, one spouse’s decision to delay Social Security can significantly impact the other’s benefits. When one spouse delays their Social Security benefits, it increases the potential survivor benefit for the surviving spouse.
This can provide more long-term security for the surviving spouse, particularly if they are in a lower income bracket or have a shorter life expectancy. For example, if a higher-earning spouse waits until age 70 to claim their benefits, the surviving spouse will be entitled to the higher payout after the higher-earning spouse’s death.
Apply for Social Security at Age 70
To apply for Social Security benefits, you must:
- Submit Your Application: You can apply online via the Social Security Administration’s (SSA) website, by phone, or in person at your local SSA office.
- Provide Relevant Documents: These may include proof of identity, work history, and bank details for direct deposit.
- Choose Your Start Date: If you’re waiting until age 70, be sure to indicate that you intend to start benefits then.

Related Links
Social Security Overseas Payments – Updated Country List Where Benefits Are Limited
Texas Sends SNAP Payments Between January 12 and 18, 2026: Check the Schedule and Beneficiaries
Is Waiting Until Age 70 Right for You?
The Social Security Age 70 Strategy can significantly boost your retirement income by increasing monthly benefits. For individuals who can afford to wait, delaying until age 70 can mean $2,500 or more a month in Social Security benefits, providing crucial financial security in retirement.
However, the decision is personal and depends on health, financial circumstances, and your overall retirement plan.
Careful consideration of your situation, coupled with financial advice, will help you make the best choice for your future. Understanding how delaying Social Security can maximize your benefits is a crucial part of planning a secure and comfortable retirement.





